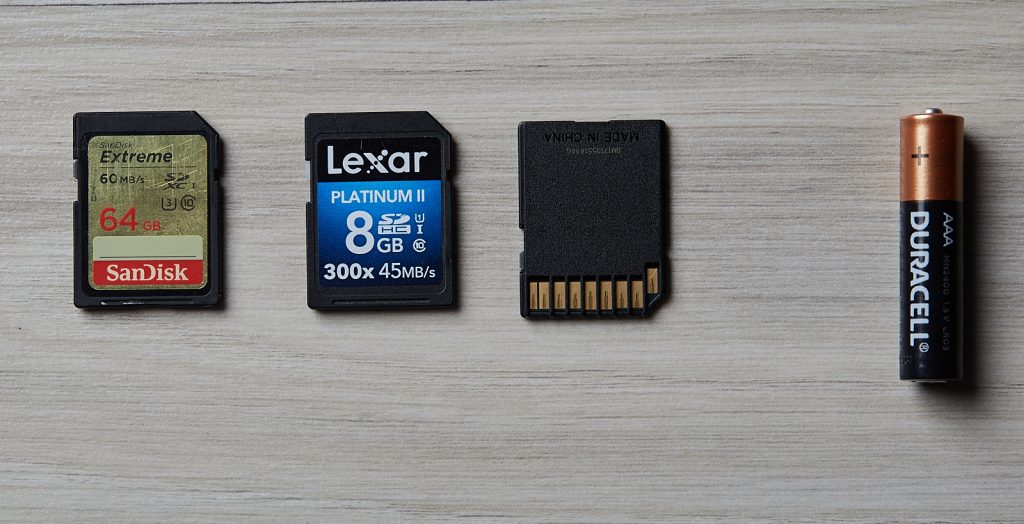
Memory cards, those tiny rectangular devices, are the silent workhorses of our digital world. From capturing precious memories on cameras to expanding the storage capacity of smartphones, they play a crucial role in our daily lives. But with a multitude of sizes and formats available, choosing the right memory card can be a daunting task. Fear not, for this comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge to navigate the maze of memory card sizes!
Understanding Storage Capacity
Let’s begin by addressing the most critical aspect: storage capacity. Memory cards are measured in gigabytes (GB) and terabytes (TB). One GB translates to roughly one billion bytes of data, while a TB is equivalent to one thousand GB. Here’s a breakdown of commonly available capacities:
- Small Capacity (2GB and under): These cards are gradually becoming obsolete due to the increasing file sizes of photos and videos. However, they might still be suitable for basic tasks like storing music on older MP3 players.
- Standard Capacity (8GB – 32GB): This is a popular range for casual users. It offers ample space for storing essential files, documents, and music collections. If you take pictures occasionally or record short videos, an 8GB or 16GB card might suffice. But for more frequent capturing or storing high-resolution content, consider a 32GB card.
- High Capacity (64GB – 128GB): This range caters to users who generate a moderate amount of digital content. It’s well-suited for photographers who capture high-quality images and videographers who shoot Full HD videos.
- Ultra High Capacity (256GB and above): Geared towards professionals and enthusiasts, these cards provide ample storage for extensive photo libraries, high-resolution videos, and even 4K footage. Some cards can even reach capacities of 1TB or more, offering immense storage potential.

Choosing the Right Format: SD, microSD, and More
Now that you understand storage capacities, it’s time to delve into memory card formats. The two most common types are:
- SD (Secure Digital): This is the standard size, typically used in cameras and digital nomads.
- microSD: As the name suggests, these are miniature versions of SD cards. They’re primarily used in smartphones, tablets, drones, and action cameras due to their compact size.
Within these formats, there are further classifications based on capacity limitations:
- SDHC (Secure Digital High Capacity): Supports capacities from 2GB to 32GB.
- SDXC (Secure Digital Extended Capacity): Handles capacities exceeding 32GB, all the way up to 2TB.
- microSDHC and microSDXC: Follow the same capacity limitations as their SD counterparts but in the microSD format.

SD vs microSD: A Matter of Size and Compatibility
When choosing between SD and microSD, size is the primary consideration. If the device has a dedicated SD card slot, it’s the preferred option due to its larger size and potentially faster read/write speeds. However, for mobile devices that lack SD card slots, microSD is the way to go.
Here’s a helpful tip: microSD cards often come with an SD adapter, allowing you to use them in devices with SD card slots. This versatility provides greater flexibility.
Beyond Capacity and Format: Speed Matters Too
While capacity and format are crucial factors, don’t overlook speed. Memory card speed determines how quickly data can be transferred to and from the card. This is especially important for tasks like capturing fast-action photos or recording high-resolution videos.
Speed classifications are indicated by two symbols: Class and UHS Speed Class. Class ratings range from 2 (slowest) to 10 (fastest), while UHS Speed Class comes in U1 (minimum 10MB/s) and U3 (minimum 30MB/s). Generally, for high-resolution photos and Full HD videos, a Class 10 or U1 card is recommended. For professional videography, especially 4K or 8K recording, a U3 card is ideal.

Integration of new technologies
Technology is no longer a collection of isolated inventions; it’s a harmonious orchestra where new advancements seamlessly integrate to create a symphony of possibilities. One such key integration is the marriage of innovative technologies like wireless connectivity with established systems, fundamentally transforming the way we interact with the world around us.
The Power of Wireless Connectivity
Wireless connectivity forms the backbone of this integration. Technologies like Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, and cellular networks have eliminated the need for physical cables, fostering a mobile and interconnected environment. Imagine a world where smart home devices communicate wirelessly, adjusting lighting and temperature based on your presence. Or picture a future where factories seamlessly exchange data with machines on the production line, optimizing efficiency through real-time communication. These are just glimpses of the transformative power of wireless integration.
Beyond Convenience: A Ripple Effect of Benefits
The benefits of this integration extend far beyond mere convenience. Wireless connectivity paves the way for the Internet of Things (IoT), a network of interconnected devices constantly collecting and sharing data. This data can be used to improve efficiency in various sectors:
- Healthcare: Wireless integration enables remote patient monitoring, allowing doctors to track vitals and adjust treatment plans in real-time.
- Transportation: Connected vehicles can communicate with each other and infrastructure, reducing traffic congestion and improving safety.
- Agriculture: Smart farming techniques, powered by wireless sensors, optimize water usage and fertilizer application, leading to sustainable food production.
Challenges and Considerations
While the integration of wireless technologies offers a plethora of advantages, there are challenges to consider:
- Security: Ensuring secure data transmission in a wireless environment is crucial. Robust cybersecurity measures are essential to prevent hacking and data breaches.
- Standardization: As different technologies come together, ensuring compatibility and smooth communication across platforms becomes paramount.
- Privacy Concerns: The vast amount of data generated by connected devices raises concerns about privacy. Establishing clear data governance frameworks is essential to safeguarding user information.
The Future Symphony: A Collaborative Effort
The integration of new technologies like wireless connectivity signifies a collaborative effort between engineers, scientists, and policymakers. By addressing the challenges and capitalizing on the opportunities, this symphony of innovation has the potential to create a more connected, efficient, and sustainable future.

Choosing the Best Memory Card for Your Needs
Now that you’re armed with knowledge about storage capacity, format, and speed, selecting the perfect memory card becomes a breeze. Consider these factors:
- Device Compatibility: Ensure the card format (SD or microSD) is compatible with your device.
- Storage Needs: Estimate the amount of data you typically store or generate.
- Transfer Speeds: If you deal with fast-action photography or high-resolution videography, prioritize higher speed classes.


